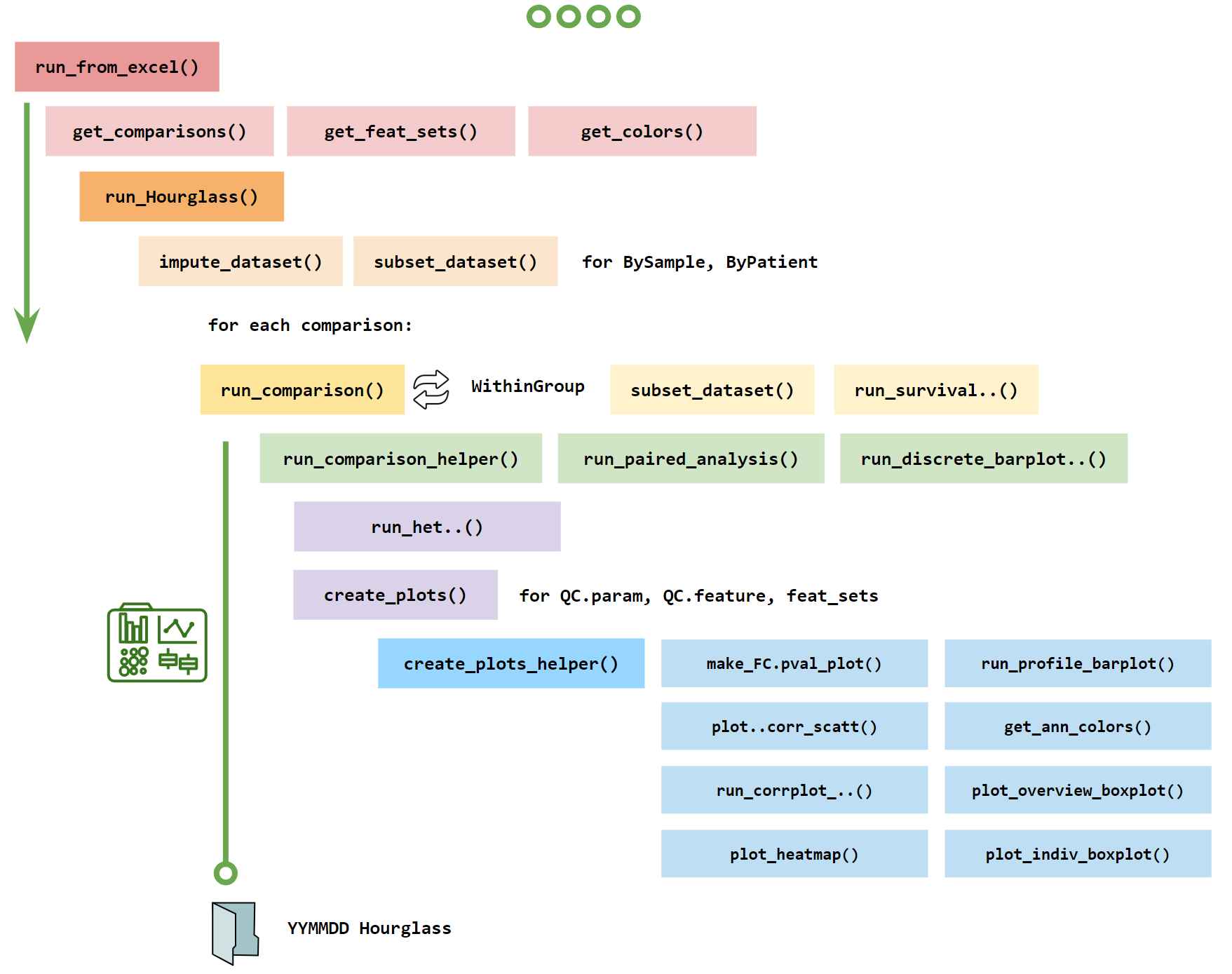
6 How to Use the R Package
We constructed new functions and compiled relevant individual data filtering functions (such as subset retrieval, imputation and outlier removal) and plotting functions (such as boxplot, heatmap, correlation matrix, survival plot visualizations).
6.2 Installation and Usage
- See Install R package (optional) for installation instructions and source code.
- Once you have installed Hourglass, load it into R using the following code:
library(Hourglass)- The best way to run Hourglass is from the Output: Excel File. Download a template here. Note: Keep in mind that all inputs are case-sensitive!
run_from_excel("path/to/excel.xlsx)Hourglass plots will be created in this directory.
6.3 Dataset Object
Note: ds = dataset
Similar to tools that explore omics and meta data structures, Hourglass characteristically takes in three data input files as part of the dataset object:
In R: dataset or ds is a list object. You can access the following elements using the $ operator.
| Element Name | Description | Data Structure | Code to Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | The name of dataset or experiment | String | ds$name |
| vals | Numeric matrix “numMat” (rows = patients/samples; columns = features/parameters) | Data frame | ds$mat |
| rowAnn | Row annotations/metadata (describes rows or samples/patients) | Data frame | ds$rowAnn |
| colAnn | Column annotations (describes columns or features of numeric matrix) | Data frame | ds$colAnn |
To create the dataset object, use Hourglass::make_dataset_ob(), and pass in 3 dataframes for vals, rowAnn, and colAnn. You may use the Hourglass::read_file() function to import tab or comma delimited files (see The 3 Files).
ds <- make_dataset_ob(
vals = read_file("ExampleData2/Example_IHC_sample_vals.csv"),
colAnn = read_file("ExampleData2/Example_IHC_sample_colAnn.csv"),
rowAnn = read_file("ExampleData2/Example_IHC_sample_rowAnn.csv"),
remove_outliers = T
)6.4 Example Dataset in R
This is a built-in dataset object in the Hourglass R package. Rename the example dataset variable (to make it smaller).
ds <- Hourglass::example_IHC_samples_dataset Since ds is a list object in R, the $ operator can be used to access individual elements (type data.frame).
Preview of each data frame:
ds$vals[1:5, 1:3] # called numMat## CD20_Area CD20_Het.Score CD20_Negative.Percent
## C0_2721_NOOBV4101T 1025027 10 58.91
## C9_2721_QCECJ5772H 2405671 1 53.44
## E4_2721_KNFYL5159D 1283798 4 NA
## G5_3420_PORPL4558C 564828 4 70.92
## B4_3327_BWDLJ3279D 1096962 1 35.22ds$rowAnn[1:5, 1:5]## Unique_ID Patient_ID TissueType Smoker Sex
## C0_2721_NOOBV4101T C0_2721_NOOBV4101T 2721 Stroma <NA> M
## C9_2721_QCECJ5772H C9_2721_QCECJ5772H 2721 Stroma <NA> M
## E4_2721_KNFYL5159D E4_2721_KNFYL5159D 2721 Stroma <NA> M
## G5_3420_PORPL4558C G5_3420_PORPL4558C 3420 Stroma <NA> M
## B4_3327_BWDLJ3279D B4_3327_BWDLJ3279D 3327 Stroma <NA> Fds$colAnn[1:3, 1:4]## Feature Parameter isNumeric Parameter_of_interest
## CD20_Area CD20 Area TRUE FALSE
## CD20_Het.Score CD20 Het.Score TRUE TRUE
## CD20_Negative.Percent CD20 Negative.Percent TRUE TRUE# Uncomment lines below to access each element
# ds$vals # 102 rows 72 columns
# ds$colAnn # 72 rows 4 columns
# ds$rowAnn # 102 rows 12 columnsAn example analysis run is provided as well (each element of the list object represents a worksheet from Output: Excel File).
example_analysis <- Hourglass::example_IHC_samples_run